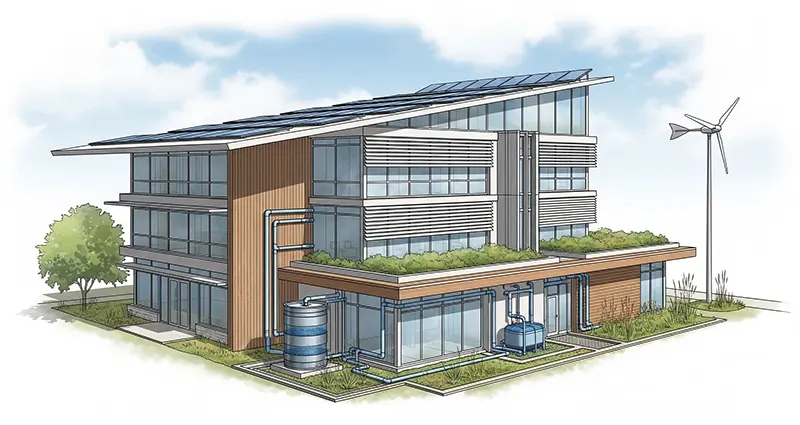
With growing concerns over climate change and rising energy costs, incorporating energy-efficient design in new building projects has become a top priority for architects, builders, and developers. Energy-efficient buildings not only reduce environmental impact but also provide long-term financial savings and enhanced occupant comfort. This article outlines practical strategies and considerations on how to implement energy-efficient design in new building projects to create sustainable, cost-effective, and healthy structures.
Understanding Energy-Efficient Design
Energy-efficient design focuses on minimizing a building’s energy consumption while maintaining optimal performance and comfort. It involves careful planning, selection of materials, orientation, insulation, and integration of energy-saving technologies.
Steps to Implement Energy-Efficient Design in New Building Projects
1. Conduct Energy Modeling and Analysis Early
Begin with energy simulation models during the design phase. These tools predict how the building will perform under different conditions and help identify areas with the greatest potential for energy savings. Using software like EnergyPlus or IES VE can optimize design decisions related to glazing, shading, HVAC systems, and lighting.
2. Optimize Building Orientation and Layout
Proper building orientation maximizes natural light and ventilation, reducing reliance on artificial lighting and air conditioning. Positioning windows to capture passive solar heat during winter and provide shading during summer can significantly improve energy efficiency.
3. Invest in High-Performance Insulation and Building Envelope
A well-insulated building envelope reduces heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. Use high-quality insulation materials for walls, roofs, and floors. Additionally, installing energy-efficient windows with double or triple glazing and low-emissivity coatings helps maintain indoor temperatures.
4. Implement Efficient HVAC Systems
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) often account for the largest portion of a building’s energy use. Select energy-efficient HVAC units sized appropriately for the building load. Incorporate smart controls and programmable thermostats to optimize system operation and reduce energy waste.
5. Integrate Renewable Energy Sources
Whenever feasible, include renewable energy technologies such as solar panels, geothermal heat pumps, or wind turbines. These systems can offset grid energy use and reduce carbon footprints. Designing buildings to accommodate future renewable installations is also beneficial.
6. Use Energy-Efficient Lighting and Appliances
Install LED lighting, which consumes significantly less energy and has a longer lifespan compared to traditional bulbs. Incorporate daylight sensors and motion detectors to adjust lighting based on occupancy and natural light availability. Choose Energy Star-rated appliances to lower energy consumption further.
7. Enhance Natural Ventilation and Daylighting
Design windows, vents, and open spaces to promote cross-ventilation, reducing the need for mechanical cooling. Maximize daylight penetration through skylights, light shelves, and reflective surfaces to improve indoor lighting quality and reduce electrical lighting load.
8. Select Sustainable Building Materials
Use materials with low embodied energy, high durability, and good thermal properties. Sustainable materials such as recycled steel, sustainably sourced timber, and low-VOC (volatile organic compound) products contribute to both energy savings and healthier indoor environments.
9. Implement Smart Building Technologies
Incorporate building automation systems that monitor and control energy use in real-time. Smart meters, sensors, and IoT-enabled devices help optimize energy consumption patterns and provide actionable data for continuous improvement.
10. Educate Stakeholders and Provide Maintenance Plans
Ensure that building occupants and facility managers understand how to operate energy-efficient systems effectively. Regular maintenance of HVAC and other equipment preserves optimal performance and energy savings over the building’s life cycle.
Implementing energy-efficient design in new building projects is a multifaceted process that requires integration of planning, technology, and sustainable practices. By prioritizing energy modeling, high-performance materials, efficient systems, and smart technologies, developers can create buildings that save energy, reduce costs, and promote environmental stewardship. As regulations tighten and sustainability becomes a market differentiator, mastering how to implement energy-efficient design in new building projects is essential for creating buildings that meet both present and future needs.