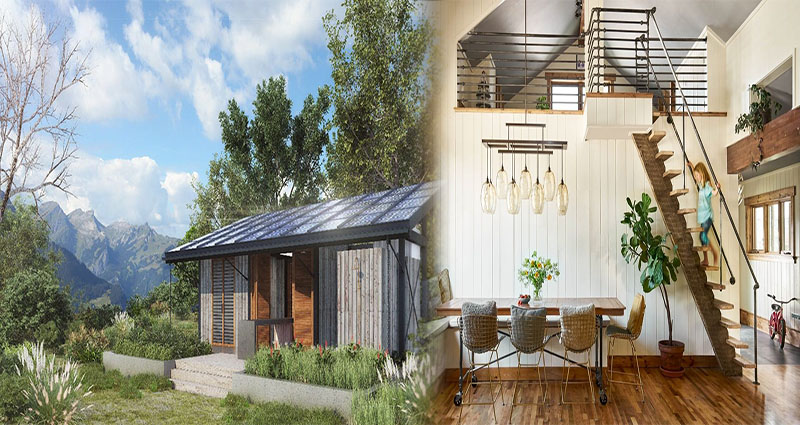
Creating Zero-Waste and Eco-Conscious Living Spaces
Living a zero-waste and eco-conscious lifestyle has become increasingly important in our efforts to protect the planet and reduce our carbon footprint. Our living spaces play a significant role in this endeavor, as they offer endless opportunities for sustainable choices and practices. By incorporating eco-friendly materials, minimizing waste, and adopting sustainable habits, we can create living spaces that not only benefit the environment but also promote well-being and healthier living. Here are some tips for creating zero-waste and eco-conscious living spaces.
1. Declutter and Simplify
Start by decluttering your living spaces. Minimalism promotes sustainable living by reducing consumption and waste. Assess your belongings and keep only what is necessary and brings joy to your life. Donate, recycle, or repurpose items that no longer serve a purpose. Adopting a minimalist approach will not only create a more open and organized space but also discourage unnecessary consumption.
2. Choose Sustainable Materials
Selecting … READ MORE ...