There’s been an explosion of new technology in the field of solar energy in recent years. Some of these new advances include Organic solar cells, Printed solar, and Polycrystalline vs. monocrystalline PV panels.
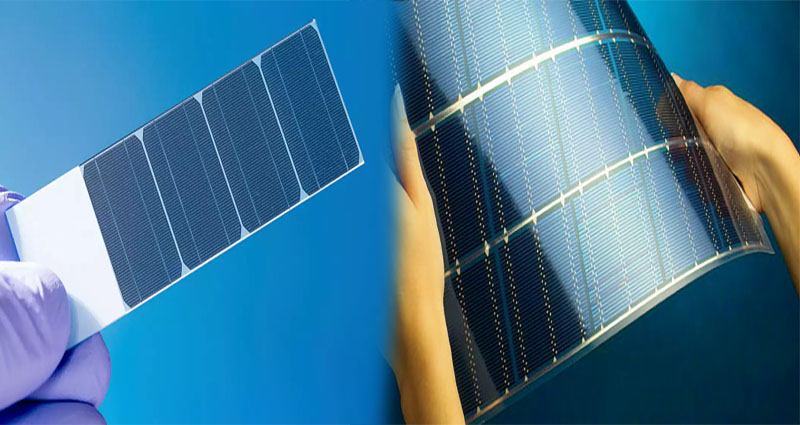
Thin solar panels
Thin solar panels are a promising new type of solar technology. These flexible cells can be printed and laminated to a variety of surfaces and are easy to transport and install. In addition, the cells produce 18 times more power per kilogram than traditional solar panels.
A new startup, Active Surfaces, has recently launched. This company has developed a thin, flexible solar cell that can be laminated to a variety of surfaces. The material, Dyneema, is an ultra-lightweight composite fabric that weighs only 13 grams per square meter. It’s also UV-curable, making it a durable and strong substance.
Other companies, such as Hanergy, are investing in research for the development of thin-film solar cells. Currently, the company has six R&D centers in the Silicon Valley area and Sichuan, China.
Organic solar cells
Organic solar cells are one of the latest advances in solar technology. They are made of carbon-based materials, like graphene, and absorb light from the sun. Their advantages include high power conversion efficiency and low cost. However, these devices still have a lot of room for improvement.
One problem that has limited organic solar cell development has been the lack of dissociation of photogenerated charge carriers. In order to overcome this limitation, researchers have proposed several strategies. Among them, a multicomponent strategy has been proposed to maximize short circuit current.
Another approach is to use p-conjugated polymers. Osaka’s team uses solution- processing to make p-conjugated polymer-based OPVs. The OPVs of this material exhibit an impressive 16-17% efficiency. It is hoped that this method can be used to improve the OPV’s efficiency in the short term.
Polycrystalline vs monocrystalline PV panels
There are many differences between polycrystalline and monocrystalline solar panels, so you need to decide what type of panel will work best for your situation. The decision is based on your budget, your preferred aesthetics, and the available space you have for your solar system.
A polycrystalline cell is made up of several crystals melted together. The resulting product is much cheaper to manufacture and can be more energy efficient.
However, it also has some shortcomings, including a higher degradation rate and a lower output when it is heated.
On the other hand, monocrystalline cells are more durable and have a longer lifetime. Moreover, they are less expensive to produce, which makes them a good choice for those on a tight budget.
Monocrystalline cells also have a better temperature coefficient than polycrystalline ones. This is a measure of how efficiently a panel works in warm weather.
Printed solar
New developments in printed solar technology could boost the solar revolution. Its versatility and ability to be used in an array of applications make it a viable alternative to the traditional silicon-based panels.
The latest in printed solar technology can be produced at low costs and with a higher efficiency than other types of solar panels. This makes them a viable option for developing countries. They are easily installed, portable, and can power houses, buildings, and even skyscrapers.
The new materials used to produce printable solar cells do not require complex, expensive materials. Unlike traditional solar panels, they do not need to be processed in high temperatures. Another advantage is that they can be easily fabricated and scaled up for large production.
Printable solar panels use electronic inks to conduct electricity. These can be deposited over metal or plastic surfaces. In addition, they can be adapted to change shape to enhance the design of a building facade.
Chinese government’s focus on renewable energy technologies
China’s government has taken a proactive approach to renewable energy development. Its policies have paid enormous dividends in the last decade. However, it is clear that China has more work to do.
The first step towards China’s low-carbon transition is to ensure that the country has a reliable source of power. Currently, China relies on coal for most of its electricity production. With the growth of technology, it can develop and install renewable energy sources.
As a result, the government has implemented subsidies that allow clean energy sources to compete with coal. This includes biogas, which is produced from waste and agricultural byproducts. Biogas is also supported by the government as part of rural development projects.
The country is working on building grid infrastructure to improve its connectivity and facilitate the integration of renewables. It will also be important to enhance electric vehicle charging and storage facilities.